As quiz 6-2 proving triangles are similar takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Delving into the intricacies of geometric shapes, this discourse elucidates the fundamental concept of similar triangles, their defining properties, and the rigorous methods employed to establish their similarity. Prepare to embark on an intellectual journey that unveils the secrets of geometric harmony and precision.
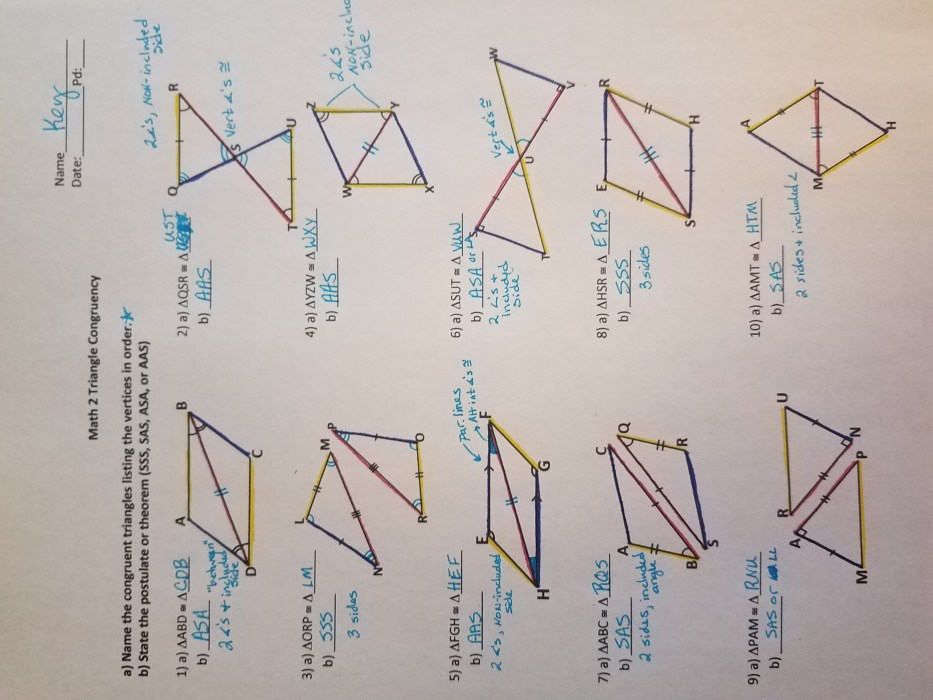
1. Introduction to Proving Triangles Similar: Quiz 6-2 Proving Triangles Are Similar
In geometry, two triangles are said to be similar if they have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. This means that the corresponding angles of the triangles are equal and the corresponding sides of the triangles are proportional.
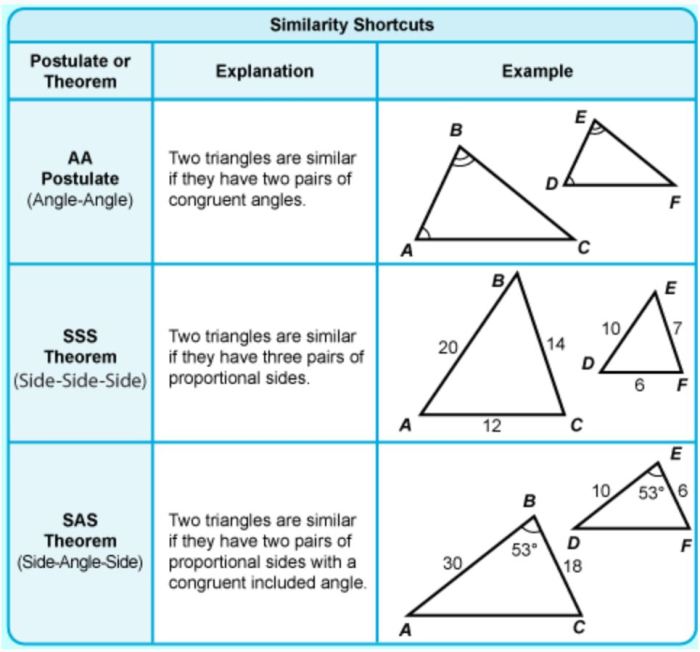
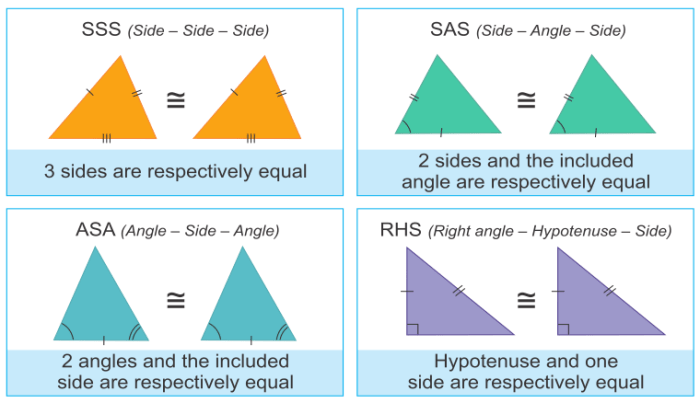
There are several methods that can be used to prove that two triangles are similar. The most common methods are the AA similarity theorem, the SSS similarity theorem, the SAS similarity theorem, and the HL similarity theorem.
2. AA Similarity
The AA similarity theorem states that if two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the triangles are similar.
For example, if triangle ABC has angles A and B congruent to angles D and E of triangle DEF, then triangle ABC is similar to triangle DEF.
| Theorem | Criteria |
|---|---|
| AA Similarity | Two pairs of corresponding angles are congruent |
| SSS Similarity | Three pairs of corresponding sides are proportional |
| SAS Similarity | Two pairs of corresponding sides are proportional and the included angles are congruent |
| HL Similarity | One pair of corresponding sides is proportional and the corresponding altitudes are congruent |
3. SSS Similarity, Quiz 6-2 proving triangles are similar
The SSS similarity theorem states that if the three sides of one triangle are proportional to the three sides of another triangle, then the triangles are similar.
For example, if triangle ABC has sides AB, BC, and CA proportional to sides DE, EF, and FD of triangle DEF, then triangle ABC is similar to triangle DEF.
| Steps | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Check if the three pairs of corresponding sides are proportional. | If they are not proportional, then the triangles are not similar. |
| 2. If the three pairs of corresponding sides are proportional, then calculate the ratios of the corresponding sides. | The ratios should be equal for all three pairs of sides. |
| 3. Use the ratios to write a proportion statement. | The proportion statement will show that the corresponding sides of the triangles are proportional. |
| 4. Conclude that the triangles are similar. | Since the corresponding sides of the triangles are proportional, the triangles are similar by the SSS similarity theorem. |
4. SAS Similarity
The SAS similarity theorem states that if two pairs of corresponding sides of two triangles are proportional and the included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar.
For example, if triangle ABC has sides AB and BC proportional to sides DE and EF of triangle DEF, and angle B is congruent to angle E, then triangle ABC is similar to triangle DEF.
- Advantage: Can be used to prove similarity even if one side is unknown.
- Limitation: Requires that the included angle be congruent.
5. HL Similarity
The HL similarity theorem states that if one pair of corresponding sides of two triangles is proportional and the corresponding altitudes are congruent, then the triangles are similar.
For example, if triangle ABC has side AB proportional to side DE of triangle DEF, and altitudes drawn from vertices B and E are congruent, then triangle ABC is similar to triangle DEF.
| Theorem | Criteria |
|---|---|
| HL Similarity | One pair of corresponding sides is proportional and the corresponding altitudes are congruent |
| AA Similarity | Two pairs of corresponding angles are congruent |
| SSS Similarity | Three pairs of corresponding sides are proportional |
| SAS Similarity | Two pairs of corresponding sides are proportional and the included angles are congruent |
User Queries
What is the AA similarity theorem?
The AA similarity theorem states that if two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the triangles are similar.
What is the SSS similarity theorem?
The SSS similarity theorem states that if the three sides of one triangle are proportional to the three sides of another triangle, then the triangles are similar.
What is the SAS similarity theorem?
The SAS similarity theorem states that if two sides of one triangle are proportional to two sides of another triangle, and the included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar.
What is the HL similarity theorem?
The HL similarity theorem states that if the hypotenuse and a leg of one right triangle are proportional to the hypotenuse and a leg of another right triangle, then the triangles are similar.