Express the balance sheets in common size percents – Expressing the balance sheets in common size percents is a valuable technique in financial analysis that allows for meaningful comparisons and insights. By converting balance sheet items into percentages of a common base, analysts can easily identify trends, relationships, and changes within a company’s financial position over time or across different entities.
This approach provides a standardized and comparable view of financial statements, enabling users to assess a company’s financial health, performance, and risk profile more effectively.
Define Common Size Percentages
Common size percentages express financial statement items as a percentage of a base amount, usually total assets for the balance sheet. This approach allows for easy comparison of financial data across companies of different sizes and industries.
The purpose of using common size percentages is to highlight the relative importance of different balance sheet accounts. By expressing all items as a percentage of a common base, analysts can quickly identify which accounts are the largest and most significant.
Methodology for Expressing Balance Sheets in Common Size Percentages
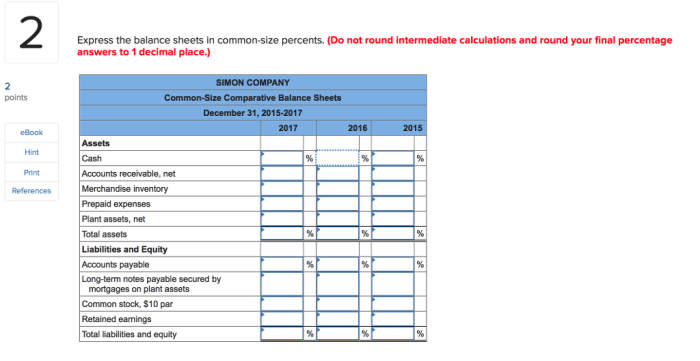
To express balance sheet items in common size percentages, follow these steps:
- Choose a base amount. For the balance sheet, total assets is typically used.
- Divide each balance sheet item by the base amount.
- Multiply the result by 100 to convert to a percentage.
For example, if total assets are $100,000 and cash is $10,000, the common size percentage for cash would be 10% ($10,000 / $100,000 x 100).
Vertical Analysis
Vertical analysis uses common size percentages to identify trends and relationships within a single balance sheet. By comparing the percentages of different accounts over time, analysts can identify changes in the company’s financial structure.
For example, an increase in the percentage of accounts receivable may indicate that the company is extending more credit to customers. A decrease in the percentage of inventory may indicate that the company is becoming more efficient in its inventory management.
Horizontal Analysis, Express the balance sheets in common size percents
Horizontal analysis uses common size percentages to compare balance sheets across different periods. This approach helps analysts identify changes in the company’s financial position over time.
For example, a company may experience an increase in the percentage of total assets held in cash. This could indicate that the company is becoming more conservative in its financial management.
Advantages and Limitations of Common Size Percentages
Advantages:
- Facilitate comparisons across companies of different sizes and industries.
- Highlight the relative importance of different balance sheet accounts.
- Identify trends and relationships within a single balance sheet (vertical analysis).
- Compare balance sheets across different periods (horizontal analysis).
Limitations:
- Can be misleading if the base amount used is not appropriate.
- May not capture all important financial relationships.
- Can be time-consuming to calculate.
Applications of Common Size Percentages
Common size percentages are used in a variety of financial applications, including:
- Industry analysis: To compare the financial structure of different companies within the same industry.
- Credit analysis: To assess the financial health of a company and its ability to repay debt.
- Investment analysis: To identify undervalued or overvalued companies.
Questions and Answers: Express The Balance Sheets In Common Size Percents
What is the purpose of expressing balance sheets in common size percents?
Expressing balance sheets in common size percents allows for meaningful comparisons of financial statements across different companies or over time, as it removes the impact of varying company sizes.
How do you calculate common size percentages for a balance sheet?
To calculate common size percentages, divide each balance sheet item by a common base, such as total assets, and multiply the result by 100.
What are the advantages of using common size percentages in financial analysis?
Advantages of using common size percentages include comparability, identification of trends and relationships, and assessment of financial performance and risk.
What are the limitations of using common size percentages in financial analysis?
Limitations of using common size percentages include potential distortion due to changes in the common base, and the need to consider other financial ratios and metrics for a comprehensive analysis.